Abstract
The Philippines participated in PISA for the first time in 2018 where the country’s participants have under-performed. Results showed consistent below-average ranking in reading, science, and mathematics literacy. In this study, we look at the possible factors that impact the dismal performance, specifically in reading.
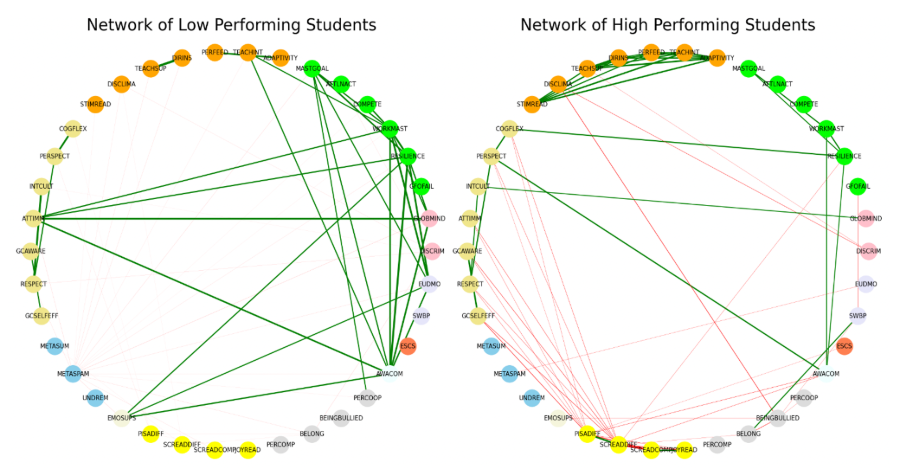
We found that intervention points can be identified when the outcome variable is included as a constituent in the network. Students’ disposition towards hard work to attain mastery is most associated to reading proficiency. Reinforcing structures were identified to provide flexibility in interventions. Also, the differences in network structures of high and low performer networks emphasize the need for a segmented approach to intervention.